|
|||
 |
 |
 |
 |
Magnetic Separation
Magnetic separators use differences in magnetic susceptibility in certain minerals to enable a separation to be made. they types of magnetic separators can be listed as follows:
Wet high intensity magnetic separators (WHIMS)
Examples of these separators are the Readings WHIMS manufactured by Mineral Technologies and Eriez WHIMS manufactured by Eriez. They are commonly used to recover / reject ilmenite from HMC ahead of dry separation. The ilmenite generally needs to be of a low TiO2 content (around 50%), so the magnetic susceptibility is high.
The Readings unit consists of a rotating carousel, which has vertically inclined salient plates through which feed slurry is passed. As the carousel rotates it passes through fields of magnetic influence generated by surrounding electromagnets, followed by fields of no magnetic influence. The magnetic grains are initially held up in the plates while the non magnetic grains are washed through into a launder below. When the plates are in the non magnetic field the magnetic grains are then wash off into a separate launder below.
In order to operate successfully the WHIMS needs to be:
The Readings WHIMS operating variables are:
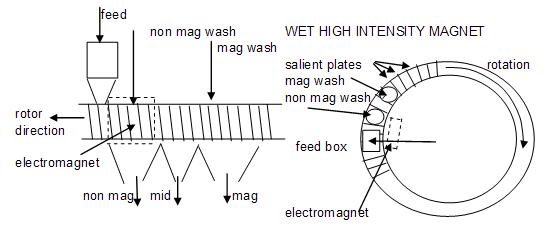
The Eriez WHIMS works on similar principles but uses a matrix that can consist of wire wool, steel balls and expanded metal.
Wet / dry low intensity magnetic drums (LIMS)
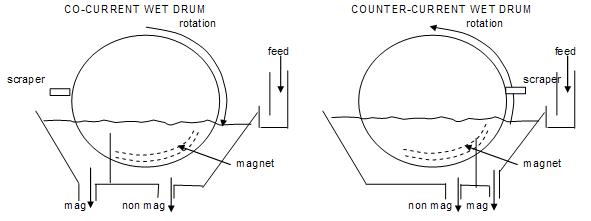
Examples of the wet separators are the Eriez LIMS manufactured by Eriez and Multotec LIMS manufactured by Multotec. They are commonly used to recover / reject magnetite from HMC ahead of high intensity wet or dry magnetic separation.
For the wet LIMS there are two models, counter-current and co-current flow. All LIMS consist of a rotating drum within which a fixed permanent magnet is located. Feed in the form of a slurry flowing through a bath, is presented to the submerged part of the drum and depending on the magnetic susceptibility of the grains is either attracted by the magnetic field and held to the drum surface or is unaffected and discharges from the bath with the slurry. As the drum rotates the magnetic grains leave the magnet field and are discharged separately usually with the aid of a scraper / brush (and spray water for the wet LIMS).
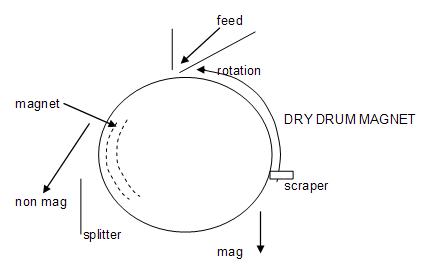
For the dry LIMS feed is distributed across the drum at the top, and as the drum rotates enters the magnetic field of a permanent magnet, with the non magnet grains being unaffected and thrown off by centrifugal force, while the magnetic grains are held to the drum surface until they leave the magnetic field and either fall or are scraped off separately.
Operating variables:
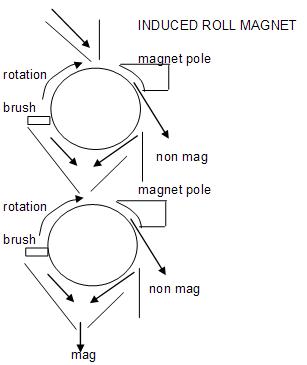
Induced roll magnetic separators (IRM)
Examples of these dry separators are the Readings IRM manufactured by Mineral Technologies They are commonly used to separate ilmenite from less magnetic and non magnetic in dry mills.
The Readings IRM consists of an electromagnet which induces a magnetic field onto a serrated rotating roll via a cast iron pole located a short distance away. Dry feed is distributed across and onto the surface of the roll at the top, where depending on the magnetic susceptibility of the grains is either held to the roll or discharges off due to the centrifugal motion of the roll. The machine has two parallel feed points, each with two rolls which are mounted vertically above each other, with the lower roll operating as a non magnetic cleaner.
Operating variables are:
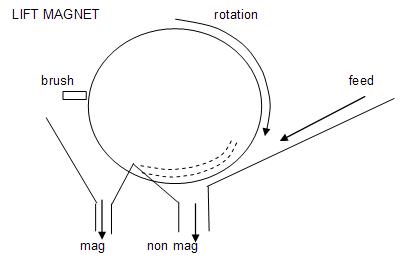
Lift roll magnetic separators
Examples of these dry separators are the Readings manufactured by Mineral Technologies. They reverse the effect of grain size (coarse magnetic grains with non magnetic grains) due to the centrifugal action of the IRM, as in this case the magnetic grains are lifted onto a rotating roll from a moving feed prior to separate discharge from the non magnetic grains which are unaffected.
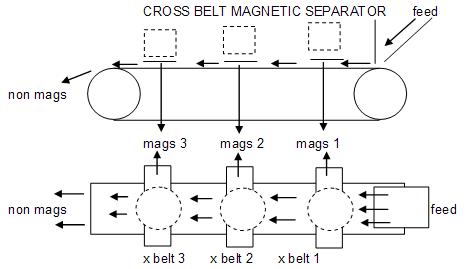
Cross belt magnetic separators
Examples of these dry separators are the Readings manufactured by Mineral Technologies. The cross belt consists of a single belt upon which the feed is distributed across and is transported slowly underneath a series of five electromagnets, the magnetic fields of which lift the magnetic grains off the belt depending on their susceptibility. Underneath each magnet is a smaller faster moving belt across the main belt at right angles which picks up the magnetic grains and transports them away from the magnetic field to discharge into launders. The gap between the main belt and the magnets becomes progressively smaller until only the non magnetic grains unaffected by the magnetic fields remain on the main belt and discharge off the end.
Operating variables include:
Disc magnetic separators
These dry separators are similar to cross belts, except that instead of using belts to transport magnetic material they employ rotating discs. Operating variables are similar. The disc magnetic separator is particularly suitable for final cleaning.
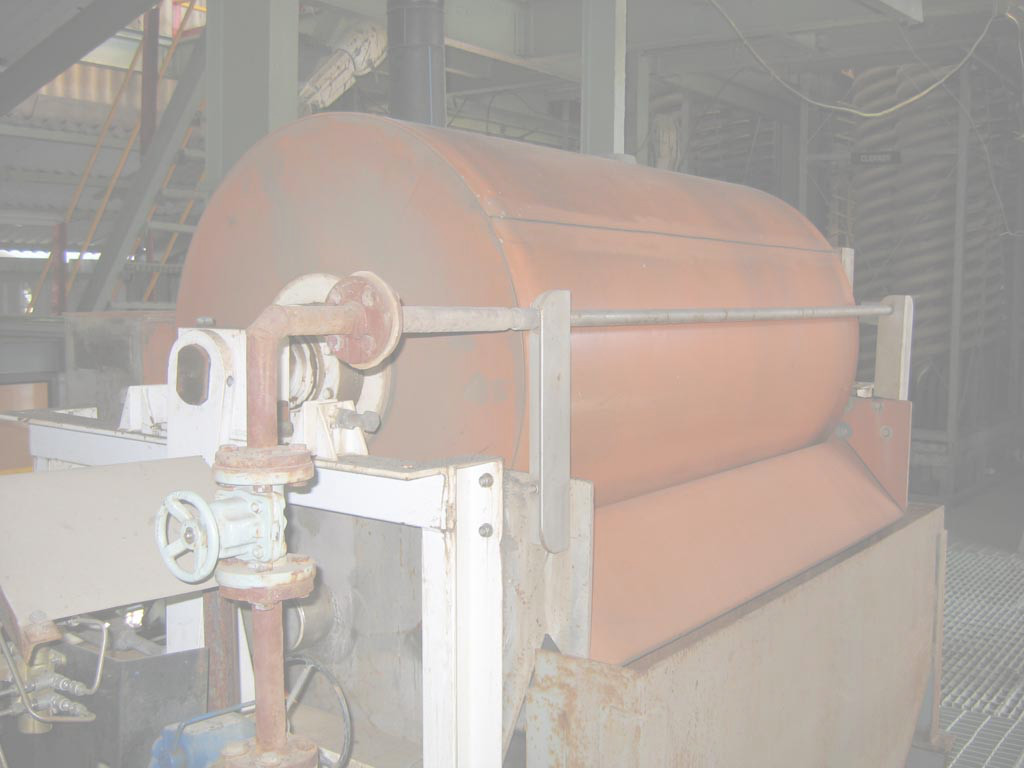
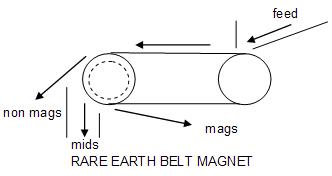
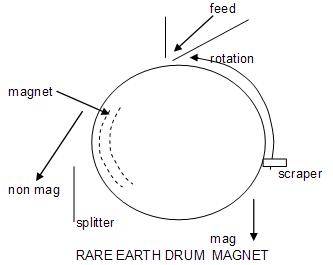
Rare earth magnetic drums (RED)
Examples of these separators are the Eriez RED manufactured by Eriez. They are similar to the dry LIMS except that they employ an exotic permanent magnet capable of producing much higher intensity magnetic field. This magnet is positioned inside a large diameter drum.
Operating variables include:
Rare earth magnetic rolls (RER)
Examples of these separators are the Eriez RER manufactured by Eriez. They differ from REDs in that they have two smaller diameter rolls between and around which a belt tracks. Feed material is distributed onto the belt which transports it to the end roll which contains an exotic permanent magnet similar to the RED. The rolls and belt move at high speed and the trajectory of the grains discharging from the belt depends on their magnetic susceptibility and the following operating variables: